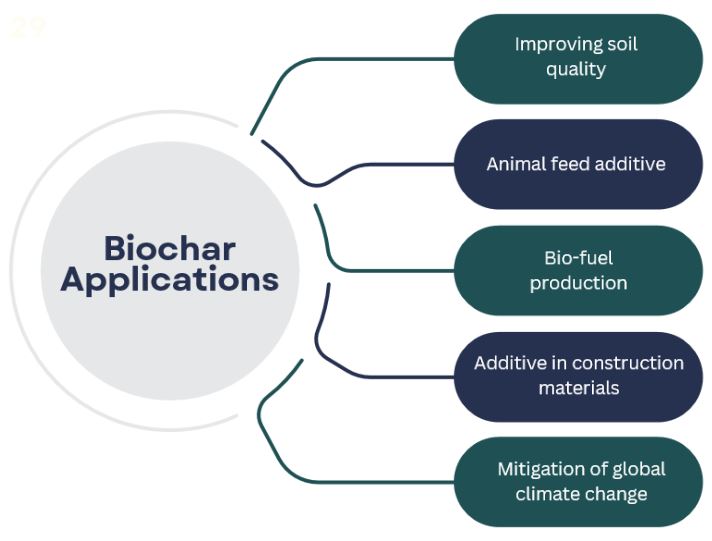
About Biochar
Biochar is a pyrogenic carbon-rich material generated from carbon neutral sources, such as biomass (Lee et al. 2017). It’s considered an excellent carbon sink as it cannot be easily decomposed by microbial activity. The International Biochar Initiative defines biochar as “a solid material obtained from the thermochemical conversion of biomass in an oxygen-limited environment”. As part of the circular economy, various feedstocks can be used to produce biochar, including wood, grass, crop residues, animal waste, sewage sludge, anaerobic digestate, bone, etc. (Alkurdi et al. 2019; Wang et al. 2020).